The Short Answer
Alternative investments encompass all investment opportunities that lie beyond the scope of conventional investment options. These are real estate investing opportunities that extend beyond fix and flip properties, buy and hold properties, rental properties and home building projects.
For those who are looking to invest in real estate, using an alternative method, here are 8 excellent alternatives which require much lower capital outlays and can easily be used to diversify your portfolio:
- Real estate crowdfunding
- Mortgage funds
- Wholesaling
- Partnerships and syndication
- Real estate investment trusts (REITs)
- Raw land
- Impact investing
- Manufactured and mobile homes
Jump To
8 Alternative Real Estate Investments That Can Deliver Good Returns
Real estate investing is one of the most successful ways to generate a profit from your investment. While traditional avenues such as residential and commercial property ownership have long been the cornerstone of wealth generation in real estate, there are alternative investments to consider, which can also deliver good returns. Let’s take a closer look at some of the alternative investments that you can consider, to navigate fluctuating markets and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
1. Real Estate Crowdfunding

Real estate crowdfunding platforms allow you to invest in real estate, without having to outlay as much capital. Instead of finding the funds to purchase a property, investors can join a crowdfunding platform like Fundrise, and invest in real estate projects with other investors, to share the financial load. These platforms allow users to invest in various real estate projects such as mixed-use properties, which gives diversity to portfolios and allows investors to choose projects based on their investment goals, risk tolerance, and preferred property types. This is one of the most popular alternative investments for investors in the digital era.
Pros
- Lower initial capital outlay as investors only need to contribute the minimum investment which can be as low as $1,000
- Flexibility for investors who can choose which project they’d like to invest in
- Diversification for real estate portfolios as investors can choose various property types and different investments
- Accreditation is not required to participate in real estate crowdfunding, which means that investors who are non-accredited can begin investing without having to worry about accreditation
Cons
- Extra fees come with crowdfunding as the platforms need to keep their resources running, as well as rules that investors need to adhere to
- There are higher risks associated with putting your money into other people’s projects, so investors will need to analyze each deal very carefully
- A lack of regulation exists in crowdfunding due to its short history and this may be an issue for some investors
2. Mortgage Funds
Mortgage funds are an alternative real estate investing path which involves a pool of mortgages that are being loaned (as mortgages) to borrowers for real estate investment projects. This allows investors to earn a profit from these projects and allows them to invest in portions of real estate, instead of having to purchase an entire property. There are various types of mortgage funds and each has their own pros and cons, such as pooled funds versus direct funds. Unlike hedge funds, mortgage funds aren’t as risky and the assets are quite specific where hedge funds are more aggressive in their aim to get the highest returns.
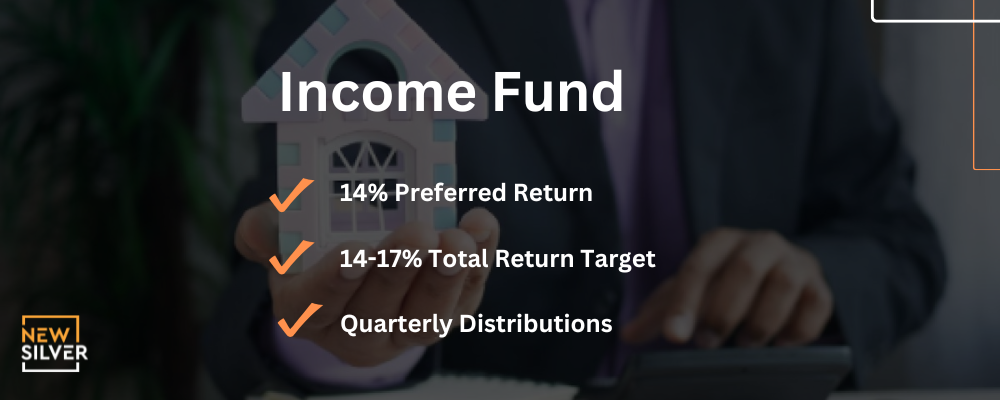
New Silver’s Income Fund is a good example of a mortgage fund where real estate investors can get access to portions of real estate, by investing a securitized pool of short duration loans originated by New Silver Lending. The preferred return on New Silver’s Income Fund is 14%, with quarterly distributions and the fund is open to accredited investors. As alternative investments go, New Silver’s Income Fund is a profitable option.
Pros
- Steady income: Investors can earn a stable income from mortgage funds which is paid in regular intervals. This provides investors with regular cash flow distributions and is a reliable source of profits.
- Diversification: Mortgage funds give investors access to a variety of real estate assets, which means that investors can get exposure to the market without direct property ownership.
- Liquidity: Mortgage funds offer investors more liquidity, unlike traditional real estate investing. This liquidity can provide flexibility for investors who may need to access their capital quickly.
- Higher returns: Mortgage funds, like New Silver’s Income Fund, can offer investors higher returns than other investing vehicles.
Cons
- Defaulting Borrowers: One of the biggest risks that comes with mortgage funds is that borrowers may default on their loan repayments. This can lead to losses for the funds and in turn investors.
- Extra fees: Mortgage funds can charge management fees, administration expenses and other extra fees. These will ultimately reduce investors’ net returns from their investments.
- Interest rates: Mortgage funds can be influenced by the interest rates, which means that this can impact the value of the underlying real estate assets. As such, the fund’s overall performance can be impacted by any changes in the overall interest rate.
3. Wholesaling

Real estate wholesaling suits those who would like to be involved in real estate but are not willing to purchase a property. This is because the concept of wholesaling involves finding a good real estate deal and selling the contract to a buyer for a fee. Wholesalers essentially facilitate the sale by finding real estate deals and pairing them with interested buyers. As such, wholesalers also need to have a good network and an eye for assessing properties quickly. This strategy allows investors to profit from real estate transactions without the need for significant capital investment or long-term ownership.
Pros
- Low capital investment: No down payment or purchase price needs to be paid, when it comes wholesaling the investment required is more around time and effort. This is a huge plus for investors who don’t want to put down a big investment but wish to participate in the real estate industry.
- Quick profit: Investors can make a quick profit from wholesaling by assigning a property to a buyer and getting paid their fee as soon as the contract is signed. Unlike traditional real estate investing, where profits can take months to be paid out, wholesaling offers a way to make profits quickly.
- Minimal risk: Since wholesalers don’t take ownership of properties, their risk exposure is limited. If a deal falls through, a wholesaler will lose out on their profit potentially, but typically not more than that or the earnest money deposit.
- Low responsibility: Unlike rental properties or fix-and-flip projects, wholesaling does not involve the ongoing responsibilities of property management, maintenance, or repairs. This can save investors time, effort, and resources, allowing them to focus on sourcing and negotiating deals.
- Potential for expansion: Wholesalers can source and sell multiple deals at once, and scale their business into something larger, to increase their earning potential.
Cons
- Market conditions: The success of a wholesaling project relies on the market conditions, which means the supply and demand in the area need to be right, the local property values need to be right and so does the investor appetite. Wholesaling can be challenging if market conditions are not favorable.
- Legal considerations: Wholesaling involves using legally binding contracts, which need to be legally compliant and uphold ethical standards. This can be a stumbling block for some, and wholesalers will need to be familiar with the laws and regulations of the area.
- Limited control: The ultimate decision for each deal lies with the buyer and seller, which means that the wholesaler has limited control. Wholesalers can only close deals if both buyer and seller agree, so the potential for delays, renegotiations, or deal cancellations exists. Leaving the wholesaler without a large amount of control over the success of the deal, other than to choose the best possible buyer for the deal.
4. Partnerships and Syndication

Investors who wish to take an alternative real estate investing path can consider partnering with other investors in a partnership or syndication to share resources and work towards a common investment goal. Each partner brings something valuable to the partnership and this can be in the form of expertise, funds, real estate deals or time and effort. Using this method, investors can gain access to a larger pool of properties than they would be able to in their individual capacity.
Pros
- Diversification: This investing avenue offers investors an easy way to diversify their portfolio and tap into different markets, property types, and asset classes. A more diversified portfolio is likely to withstand more economic changes than one which hinges on a single type of investment.
- Lower risk: Investors can spread the risk among partners and improve the success and resilience of their portfolio.
- Economies of scale: Pooling resources with other investors allows for the benefits of economies of scale to be realized. This means that investors can save on costs, maintenance and financing by splitting the expenses, and it may also lead to higher overall returns.
- Passive income: Typically, partnerships involve a passive role, which means that partners can generate a passive income from their real estate investments. Investors can benefit from the rental income distributions and potential capital appreciation, without having to be very hands-on.
Cons
- Disputes: Any partnership will be at risk of disputes between partners. These disputes can be around investment strategy, asset management or distribution policies. Partners need to have clearly defined agreements, roles and distribution policies in order to avoid conflict wherever possible.
- Distribution uncertainty: The distribution amounts and timing may vary, due to property performance, market conditions, and operating expenses. This means that partners may not have a steady, reliable cash flow from this method of real estate investing.
- Limited control: Partners need to agree on their decisions, so this means that some partners will need to relinquish control over certain investment decisions. For some people, this can be a challenge.
- Not liquid: Partnerships or syndications can tie up partners’ funds for a certain period of time. Which means that if they need access to these funds in a hurry, they may not be able to sell their investment or exit the deal before the specified holding period is completed.
5. Real Estate Investment Trusts

A real estate investment trust (REIT) is provided by a company that owns, operates or finances income-generating real estate, and these are traded on major stock exchanges typically. REITs allow investors to purchase shares of properties and earn an income through dividends on this. The properties that are included in a REIT portfolio range from apartment complexes to hotels and more. Essentially, a REIT collects the rent from each property and this is distributed to investors as dividends. There are various types of REITs that investors can choose from, depending on their investing strategy, including residential, retail, healthcare and office REITs.
Pros
- Accessibility: The liquidity provided by the nature of REITs being traded on the stock market means that investors can get easier access to their investment. This provides investors with a more liquid form of real estate investment than traditional investing avenues.
- Steady income stream: REITs are an attractive option for investors who are looking to generate a steady stream of income, because they are required by law to distribute the majority of their taxable income to their shareholders, which means that dividends are paid regularly.
- Professionally managed: REITs are usually managed by real estate professionals who are experts in their fields of property acquisition, leasing and asset management. For REIT investors, this means that their investment is in good hands, and they can enjoy maximized returns from experienced professionals who are looking to optimize each property’s performance.
- Portfolio diversification: REITs give investors the opportunity to expand their portfolio, without having to make any significant purchases. The diverse range of properties offered by REITs allows investors to spread the risk on their portfolio and enhance its resilience during market fluctuations.
Cons
- Market changes: REIT performance is closely tied to real estate market conditions and investor sentiment. Economic downturns, fluctuations in interest rates, and changes in property values can impact REIT share prices and dividend yields, leading to volatility in returns.
- Management fees: While REITs are typically run by experienced real estate professionals, this comes at a fee. Management fees are often charged to those investing in REITs, which can reduce their returns.
- Dividends taxed as income: The dividends that are paid out to REIT shareholders are taxed as regular income, which means that investors may face a higher tax burden on REIT income, than other investment avenues.
6. Raw Land

Investing in raw land gives investors a few options, they can either sell it as is, they can build a property, they can lease it, or use it for agricultural purposes. Raw land denotes parcels of land that are in their natural state, devoid of development, improvements, or essential utilities and infrastructure. Successful investment in raw land requires thorough research on the location, careful consideration of zoning laws and regulations, and hiring the right professionals.
Pros
- Appreciation in value: The supply of raw land is not infinite, which means that over time the value of the land will increase. As the demand for land in an area increases, so does its value, and this is where investors can capitalize.
- Low holding costs: Raw land has lower maintenance costs than developed land, and this is a major saving for investors. There are no repairs or renovations to do, and no buildings to maintain, which is a cost saving.
- Flexibility: Raw land provides investors with a significant amount of flexibility in terms of uses and development. Investors can subdivide the land and use it for multiple purposes, or hold onto it for future use, or explore various development options like agriculture, residential properties and more.
- Easy acquisition: Acquiring raw land is typically an easier process than buying developed it. It involves fewer legal prerequisites and entails a less complex purchasing process, which makes it an appealing choice for investors.
Cons
- No immediate income: Unlike developed land which can begin earning an income immediately, raw land cannot provide an immediate income. In fact, it may be some time until you can earn an income from raw land.
- Zoning restrictions: The local zoning laws may prohibit development of a certain type on the raw land, which can hinder your plans for it. Before buying raw land, you should make sure you’re aware of the area’s zoning laws and how this impacts your plans.
- Permits: Several permits may be required in order to develop the raw land. These permits can be costly, and time consuming to acquire. Permits can be required for driveways, building and construction, septic development and more.
- Time: Buying raw land is not a quick process, investors will need patience and devote a longer time to the process in order to begin making a profit from it. The land will first need to be developed, then prepared and this can take a while to get it rent-ready or sell-ready. Only once the property is sold or rented, does it become profitable.
7. Impact Investing

Instead of investing in a real estate venture purely to make money, impact investing is a good way to earn a profit while also improving the investment’s environmental or social impact. Impact investing in real estate can take the form of affordable housing, sustainable communities, and green real estate. These projects can provide housing to those in the lower-income bracket, or creating future growth in an area, or creating projects with higher environmental standards.
Pros
- Positive social and environmental impact: Impact investing in real estate enables investors to address pressing social and environmental challenges while earning financial returns. These investments have the potential to create positive change and contribute to sustainable development goals.
- Alignment for goals and values: This investing strategy allows investors the chance to combine their financial goals with their personal values and social or environmental priorities. This means they can support the causes that are meaningful to them and make a real difference.
- Long-term sustainability: Real estate investments that address social and environmental issues tend to be more resilient over the long term, because they’re working towards a goal that can increase property values and create stability in communities.
Cons
- Impact assessment: Fully assessing the social and environmental impact of these real estate investments can be difficult. There are no standardized reporting metrics for assessing this, and it can be challenging to quantify the impact that has been made.
- Financial goals: Sometimes impact investing involves making a lower profit, to make a greater impact. It can be difficult to meet your financial goals with this type of investment.
- Regulations and policies: Navigating the legal frameworks around these projects can be tricky. This involves zoning regulations, building codes, and environmental laws, which need to be adhered to, for successful projects to be completed.
8. Manufactured and Mobile Homes

With the trend towards affordable housing becoming more prominent, manufactured and mobile homes are alternative investments that can be lucrative. The strategy involves purchasing manufactured and mobile homes, then renting them out. These homes are typically prefabricated and can be located in mobile home parks or other communities that offer affordable housing.
Pros
- Affordable: This real estate investment option is more affordable and offers investors the chance to purchase multiple manufactured or mobile homes thanks to the cheaper price tag on these.
- Steady income: These homes offer investors a steady stream of income. While it may be lower than some other investment types, it still helps cash flow to retain a regular rental income.
- Easy upkeep: Manufactured and mobile homes generally don’t require extensive maintenance, so real estate of this nature is generally easier and cheaper to maintain.
Cons
- Location challenges: The location of manufactured and mobile homes can significantly impact their desirability and rental rates. Investors should carefully evaluate the local market dynamics, including demand, vacancy rates, and rental trends, before investing.
- Limited financing options: Finding funding for real estate projects like this can be more challenging than traditional investment options. Lenders may require higher down payments or have strict qualification criteria.
- Land leasing fees: Mobile homes may be located on land that requires a fee to lease, which means that investors need to outlay the funds for this. These can include ongoing lease fees which can impact an investor’s overall return on investment.
Which Option Is Best For You?
Choosing the right alternative investments for you depends on your financial and personal goals. So, it’s important to thoroughly research these alternative investments and be aware of the benefits and challenges. However, here’s a general guideline:
1. Crowdfunding – Suited to those who are looking for a passive income opportunity with a lower initial capital outlay
2. Mortgage Funds – Best for investors who are looking for a steady cash flow with good returns and a lower risk
3. Wholesaling – Ideal for entrepreneurial real estate investors who have a flair for negotiation and a thorough market knowledge
4. Partnerships and syndication – For investors who are accredited, or high net worth individuals who are looking to pool resources with other investors
5. Real estate investment trusts (REITs) – Suited to investors who would like to have a hands-off approach and exposure to real estate without the need to own property outright
6. Raw land – This strategy suits investors who are in it for the long haul, and are willing to accept more risk for more potential gain
7. Impact investing – Investors who have a strong personal interest in social and environmental impacts, and wish to combine this with their financial goals should consider this option
8. Manufactured and mobile homes – This option is ideal for those who want affordable real estate investments with a steady income stream, but who understand the market fluctuations